- Published on
GitHub Enterprise Server Explained
- Authors

- Name
- Gabriel
- @gabriel__xyz
GitHub Enterprise Server is the self-hosted version of GitHub, designed for organizations that need total control over their development environment. Think of it as your own private, secure fortress for code, but instead of being in the public cloud, it's deployed right on your own infrastructure. This approach is a game-changer for companies with strict security and compliance mandates.
Your Private Software Development Fortress

Imagine your company's source code is its collection of secret recipes—its most valuable intellectual property. Using a cloud service is like storing those recipes in a shared, high-security commercial kitchen. It's safe, but you don't own the building.
GitHub Enterprise Server, on the other hand, is like building your own state-of-the-art culinary lab on your own land, complete with a moat and high walls. You control every lock, every entry point, and every single process that happens inside.
This self-hosted platform is far more than just a code repository; it's a complete DevOps environment that you manage from the ground up. Since it first launched back in 2011, it has become a cornerstone for enterprises in highly regulated fields like finance, healthcare, and government, where data sovereignty is absolutely non-negotiable.
In fact, over 90% of Fortune 100 companies use GitHub in some form, often striking a balance between cloud and on-premises deployments to meet a wide range of regulatory demands. You can find out more about its adoption in regulated industries to see how it's used in the real world.
GitHub Enterprise Server vs GitHub Enterprise Cloud At a Glance
So, what's the real difference between running your own server and using GitHub's managed cloud service? This table breaks down the key distinctions.
| Feature | GitHub Enterprise Server | GitHub Enterprise Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Hosting | Self-hosted on your own infrastructure (on-premises or private cloud) | Hosted and managed by GitHub on their cloud infrastructure |
| Control | Complete control over the environment, data, and security policies | Managed by GitHub; less direct control over the underlying infrastructure |
| Compliance | Ideal for strict data residency and regulatory needs (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) | Meets many compliance standards, but data resides on GitHub's servers |
| Maintenance | Your team is responsible for updates, backups, and maintenance | GitHub handles all maintenance, updates, and infrastructure management |
| Customization | Highly customizable to integrate with your existing internal tools and security stacks | Less customizable; integrations are primarily through the GitHub Marketplace and APIs |
| Internet Access | Can be run in a fully air-gapped environment with no internet access | Requires a stable internet connection for access |
| Feature Updates | Updates are applied manually by your team on your own schedule | Receives the latest GitHub features and beta access automatically |
| Best For | Organizations with stringent security, regulatory, and data sovereignty requirements | Teams that want the latest features and minimal maintenance overhead |
Ultimately, the choice comes down to how much control your organization needs versus how much operational overhead you're willing to manage.
Why Choose a Self-Hosted Solution
The decision to run your own instance almost always comes down to a handful of critical needs that public cloud services can't quite meet. Opting for an on-premises solution gives your organization some major advantages, especially when it comes to protecting your operational integrity.
These core benefits are designed to solve the biggest challenges for organizations handling sensitive data. They offer peace of mind that your most critical digital assets are safe within an environment you own and operate.
The primary driver for adopting GitHub Enterprise Server is control. It gives you the final say over security policies, data location, and toolchain integrations, ensuring your development lifecycle aligns perfectly with your business rules.
For any organization where compliance isn't just a suggestion but a hard requirement, this level of authority is indispensable. It transforms your development platform from a third-party service into a core piece of your internal infrastructure, held to your own rigorous standards.
Understanding the Core Architecture
To really get what makes GitHub Enterprise Server tick, we need to pop the hood and look at how it’s built. At its core, the platform isn’t just a piece of software you install; it's a powerful, self-contained virtual appliance.
Imagine getting a complete, pre-packaged city-in-a-box that you can just drop onto your own digital land—whether that's your on-premise infrastructure or your private cloud. This appliance is designed to run on all the major players: VMware, AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud Platform. This gives you the freedom to plug it right into your existing IT setup, combining the polished feel of GitHub with the rock-solid control of hosting it yourself.
This concept map gives a nice visual of how all the pieces fit and work together.
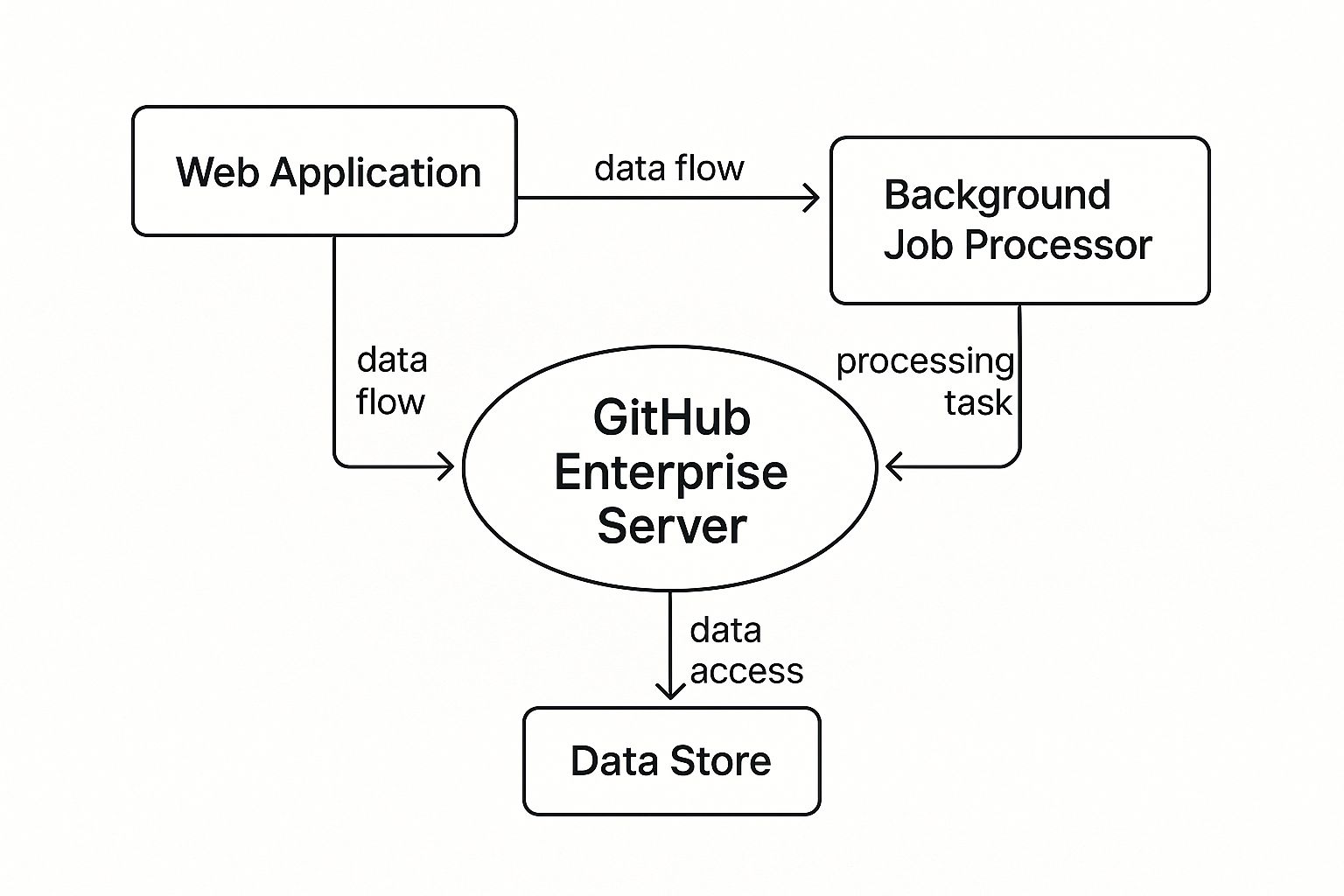
As you can see, it's a symbiotic system. The web application is what you see and interact with, but it cleverly offloads the heavy lifting to a background processor. All the while, the data store acts as the system's memory, keeping everything organized and accessible.
The City Planning Analogy
A great way to wrap your head around this architecture is to think of it like a well-planned city. Every component has its own job, but they all work in harmony to create a self-sufficient ecosystem for your developers. Each part is critical to keeping the city running without a hitch.
This design makes sure different kinds of work don't step on each other's toes, which is key to keeping the platform stable and snappy. Let's take a tour of the main "districts" in this city.
Key Architectural Components
The GitHub Enterprise Server appliance is built on a few foundational pillars, each handling a specific function. These parts are finely tuned to operate in concert, creating a smooth experience for both the people using it and the admins managing it.
The Web Application: This is the city's downtown—the bustling commercial and residential district where everyone hangs out. It's the user-facing part of the platform where developers live, interacting with repos, pull requests, and issues. Built on Ruby on Rails, it handles all those real-time interactions and serves up the GitHub interface we all know.
Background Job Processors: Think of this as the city's industrial park, humming with activity behind the scenes. It takes on all the heavy-duty tasks like firing off email notifications, building search indexes, or running pre-receive hooks. By pushing this work to the background, it keeps the web application free and responsive for users.
The Data Stores: This is the city's infrastructure and archives—the record-keeping hall and the library. It uses MySQL for relational data like users, permissions, and issues, and leans on Elasticsearch to power its incredibly fast code search. This two-pronged approach is optimized for both transactional integrity and speedy, indexed searching.
Just like a city separates its residential zones from its industrial factories, GitHub Enterprise Server separates its functions. This design prevents a massive background job, like re-indexing a huge repository, from slowing down a developer trying to merge a critical pull request.
This modular architecture is the secret sauce that allows GitHub Enterprise Server to pack in powerful features and deliver reliable performance, all from within the safety of your own network. Each piece is essential to building a development hub that just works.
Securing Your Development Lifecycle

When an organization decides to go with GitHub Enterprise Server, one reason usually stands out above all others: security. Sure, hosting your code on your own infrastructure is a great first step, but the real magic is in the deep, multi-layered security features that guard your intellectual property from the first line of code to the final deployment.
It all starts with controlling who can touch what. The platform offers powerful role-based access controls (RBAC), letting you set up incredibly detailed permissions for individual users, teams, and entire organizations. You get to decide who can read, write, or administer repositories, making sure developers have just enough access to do their jobs—and nothing more.
To lock things down even tighter, GitHub Enterprise Server plugs right into your company's existing identity systems. It connects smoothly with SAML or LDAP directories, so user authentication is handled by the same central system you already trust. This approach unifies logins and makes adding or removing team members a secure, straightforward process. For an even better developer experience, you can look into methods for streamlining Git CLI authentication without putting credentials at risk.
Proactive Threat Detection with Advanced Security
Beyond managing access, the platform is designed to help you find and squash vulnerabilities long before they ever see the light of day. This is where GitHub Advanced Security (GAS), an optional add-on, completely changes the game. It’s a suite of tools that runs entirely inside your private environment, keeping your code and security analysis self-contained.
GAS gives you a proactive security posture through three core features:
- Code Scanning (CodeQL): Think of this as an automated security expert who reviews every line of code you push. It automatically scans for potential security holes and common coding mistakes, flagging things like SQL injection flaws or cross-site scripting risks right inside the pull request.
- Secret Scanning: This tool is like a digital watchdog for your repositories. It constantly scans for accidentally committed secrets—API keys, tokens, private certificates, you name it. If it finds one, you get an immediate alert so you can revoke the credential before anyone can misuse it.
- Dependency Review: Let's face it, modern apps are built on a mountain of open-source packages, and each one is a potential backdoor. This feature scans your dependencies for known vulnerabilities and license compliance issues, helping you keep your software supply chain secure. You can learn more by checking out our detailed comparison of popular tools like Dependabot vs Renovate in our guide.
Enforcing Security at Every Commit
These tools are powerful on their own, but they're most effective when you bake them into your daily workflow with security policies. For instance, you can set up repository rules to automatically block a pull request from being merged if CodeQL finds any high-severity vulnerabilities.
Imagine a developer accidentally tries to commit a file containing a production AWS key. With secret scanning push protection enabled, GitHub Enterprise Server will automatically block the push and alert the developer to remove the secret before it ever enters the repository’s history.
This "shift-left" approach transforms security from a reactive chore into a proactive, developer-first habit. By building these guardrails directly into the development process, GitHub Enterprise Server helps you ensure your code isn't just innovative, but fundamentally secure from the very start.
How the Pros Use It to Win
Okay, so we've talked features. But the real magic of GitHub Enterprise Server comes alive when you see how top companies actually use it in the wild. Its impact is most obvious in industries where things like compliance, security, and stability aren't just nice-to-haves—they're non-negotiable.
For these organizations, GHES isn't just another tool in the stack. It's a strategic advantage that lets them stay competitive while playing by some very strict rules. The self-hosted model gives them the power to build a development ecosystem that’s both incredibly capable and entirely under their lock and key.
Nailing Security in Regulated Industries
Think about sectors like finance or healthcare, where compliance is king. A financial firm has to live and breathe PCI DSS to protect cardholder data. A healthcare company is bound by HIPAA to keep patient information secure. There's no room for error.
This is where GitHub Enterprise Server becomes a fortress. These companies use it to build a completely fortified development environment. Here’s a peek at how they pull it off:
- Enforcing Strict Commit Policies: They use pre-receive hooks—basically, custom scripts that run on the server before a push is accepted. A common one is a script that automatically rejects any commit that doesn't have a valid Jira ticket number. This simple rule ensures every single code change is tied to a documented task. No exceptions.
- Integrating with Internal Systems: They wire up the server to their own internal tools, like a private Jenkins instance for CI/CD or custom-built security dashboards. This creates a closed-loop, automated workflow where code is built, tested, and scanned, all without ever leaving their secure network perimeter.
- Using Audit Logs for Compliance: When regulators show up, audit logs are their best friend. They provide a perfect, unchangeable record of everything that happened on the platform. Companies can instantly prove who touched what code, when they did it, and that all the right security protocols were followed. It turns a painful compliance audit into a straightforward check-the-box exercise.
A government agency, for instance, can maintain absolute control over code related to national security. By running GHES in a completely "air-gapped" environment, they guarantee that their most sensitive intellectual property never, ever touches the public internet.
This level of control allows these organizations to innovate without compromising on safety. It’s also why many of them end up saving money by consolidating their toolchains. One major food and beverage company, for example, retired at least nine legacy systems after switching to GitHub Enterprise. Meanwhile, a financial firm used GitHub Advanced Security to boost its application security coverage from under 20% to over 80%. You can dig into more of these GitHub statistics and their business impact.
Supercharging Developer Speed and Efficiency
While security is a massive driver, efficiency is right up there with it. The best engineering teams know that the less friction in the development process, the faster they can innovate.
GitHub Enterprise Server is built for this. It allows for deep integrations that cut out manual work and streamline workflows. By connecting GHES to internal systems, teams can automate away the boring, repetitive tasks and just focus on what they do best: writing great code. If you want to see what this looks like at an elite level, check out our post on how Stripe ships over a thousand pull requests daily.
Managing Your Self-Hosted Instance
Running your own GitHub Enterprise Server instance is like getting the keys to your own private development kingdom. It gives you incredible control, but it also means you’re in charge of maintaining the castle walls. Proper administration is the bedrock of a stable, secure, and snappy self-hosted environment.
The day-to-day work is real. You'll need to be on top of everything from onboarding new developers to having a solid plan for when things go wrong. Admins have a lot on their plate to keep the platform running smoothly for everyone who depends on it.
Core Administrative Duties
Your main command center for all this is the Management Console, a web-based interface that puts all the controls at your fingertips. From here, you’ll configure settings, push out updates, and keep an eye on the system’s health. Managing your GitHub Enterprise Server instance effectively is a key part of your company's broader enterprise IT asset management strategies.
Here are the big tasks admins juggle:
- Initial Setup and Configuration: This is ground zero—deploying the virtual appliance, configuring the network, and setting up critical services like SMTP so developers actually get email notifications.
- User Management: This involves hooking into your company’s authentication systems (like LDAP or SAML), creating user accounts, and defining who can do what.
- System Upgrades: Keeping your instance updated with the latest security patches and features isn't a surprise—it's a planned event. You’ll need to schedule maintenance windows and follow the upgrade playbooks carefully.
- Monitoring and Health Checks: It's all about being proactive. You’ll need to watch system resources, hunt for errors in the logs, and make sure background jobs are chugging along. This stops tiny hiccups from turning into full-blown outages.
The real power of self-hosting lies in your ability to shape the environment to your exact needs. However, this also means the buck stops with you when it comes to backups, security, and uptime.
Key Administrative Responsibilities
For anyone stepping into this role, it helps to see the responsibilities laid out. The table below breaks down the main task areas, what they involve, and the tools you'll be using.
| Task Area | Key Responsibilities | Tools Used |
|---|---|---|
| Setup & Configuration | Deploying the appliance, setting up networking, configuring SMTP, and establishing initial security settings. | Management Console, Hypervisor (VMware, Hyper-V) |
| User & Access Control | Integrating with LDAP/SAML, managing user accounts, setting repository permissions, and defining organization policies. | Management Console, ghe-user-manage CLI |
| Maintenance & Upgrades | Applying patches, performing version upgrades, scheduling maintenance windows, and communicating downtime to users. | Management Console, ghe-upgrade script |
| Monitoring & Logging | Tracking CPU/memory usage, reviewing system logs (/var/log/github), and ensuring background services are running smoothly. | top, htop, ghe-diagnostics, External monitors |
| Backup & Recovery | Scheduling regular backups, testing the restore process, and having a clear disaster recovery plan in place. | GitHub Enterprise Server Backup Utilities, Cron jobs |
Ultimately, a well-managed instance becomes a silent partner in your development process, empowering teams instead of slowing them down.
Planning for Resilience and Scale
Beyond the daily grind, a huge part of managing GitHub Enterprise Server is planning for the unexpected and getting ready for growth. A great instance isn’t just stable today—it’s tough enough to handle whatever comes next.
This forward-thinking approach boils down to two things: disaster recovery and scalability. For teams spread across the globe, giving everyone fast, reliable access is everything.
To build an instance that's both tough and ready to grow, admins focus on:
- Backups and Disaster Recovery: A solid backup strategy isn't optional. Using tools like the GitHub Enterprise Server Backup Utilities is a must. This means regular snapshots and, even more importantly, actually testing your restore process to make sure you can get back online quickly if something goes sideways.
- High Availability (HA): For instances that are absolutely critical to your business, you'll want to configure a failover replica. In an HA setup, a passive replica instance is always on standby, ready to take over automatically if the main one fails. It's your secret weapon for minimizing downtime.
- Geo-Replication: If your teams are all over the world, geo-replication is a game-changer. It sets up active replicas in different geographic locations. This means developers in another country can pull code from a nearby data center, slashing latency and giving them a much faster experience.
Nailing these responsibilities ensures your self-hosted instance remains a powerful asset—not an operational headache—and can support your teams as they continue to grow.
Integrating with Your DevOps Toolchain
A self-hosted platform like GitHub Enterprise Server shouldn't feel like it's on an island. It’s built to be the central hub of your DevOps ecosystem, plugging right into the tools your team already uses and loves. This is huge, because it means you get to enhance your existing workflows instead of rebuilding them from scratch.
So, how does it pull this off? Through two key pieces of tech: webhooks and a powerful API. Think of webhooks as automated messengers that shout updates to other apps whenever something happens—like a new commit or a merged pull request. The API, on the other hand, lets you build much deeper, custom integrations to pull data and automate all sorts of complex tasks.
Connecting Your Favorite Tools
This flexibility lets you wire everything together into one smooth, automated toolchain. For instance, you can connect your instance directly to:
- CI/CD Pipelines: Automatically kick off builds in tools like Jenkins or CircleCI the second new code is pushed.
- Project Management: Keep your Jira tickets in sync by automatically updating them when a pull request is opened or closed.
- Communication Platforms: Ping a specific Slack channel when a developer is up for a code review.
This kind of automation is the secret sauce for creating really efficient development cycles. If you want to dive deeper into automation, check out our guide on how to create reusable GitHub Actions in 2025.
By connecting your essential tools, GitHub Enterprise Server becomes more than just a place to store code. It turns into a command center that orchestrates your entire software development lifecycle, from the first commit all the way to deployment.
You'll also find specialized tools built on top of these integrations to solve very specific problems.
Take PullNotifier, for example. It uses these very connections to build smart, custom notification workflows. This ensures the right people see the right updates in Slack without all the extra noise. At the end of the day, bringing GitHub Enterprise Server into your stack is all about amplifying the tools you already have, not replacing them.
Common Questions About GitHub Enterprise Server

Jumping into a self-hosted solution like GitHub Enterprise Server always raises a few practical questions. It's one thing to know the features, but another to understand how it fits into your day-to-day operations.
One of the first things people ask is about the upgrade process. Since you’re in the driver’s seat, your team handles all the updates. You can apply them through the Management Console, which gives you the freedom to schedule everything during planned maintenance windows. This means no surprises—you can test new versions in a staging environment before they ever touch production.
Then there's the question of migration. How do you get your existing repositories off platforms like Bitbucket or GitLab and onto your new server? GitHub has official importers and tools designed to make this as painless as possible. They do a great job of preserving commit history, branches, and other critical data, so your teams can pick up right where they left off. A little bit of planning goes a long way here.
Licensing and Support Details
Of course, you have to think about the business side of things, too. How does GitHub Enterprise Server licensing actually work? It’s pretty straightforward.
- Per-User Licensing: It’s a subscription model, typically billed per user, per year. If a developer needs access to the instance, they need a license. Simple as that.
- Bundled Features: The license packs in all the core features you’d expect. You can also bolt on extras like GitHub Advanced Security if you need more robust threat detection.
And what happens when something goes wrong? That's where GitHub Enterprise Support comes in. You get a dedicated team to help with technical snags, from troubleshooting and configuration questions to best practices for keeping your instance running smoothly. Having that expert backup is crucial for making sure your platform stays reliable and secure.
Thinking through these practical details—upgrades, migration, licensing, and support—helps you see the full picture. It’s not just about whether the technology is a fit, but whether the entire solution aligns with your team’s workflow and budget.
Stop letting pull requests get lost in the noise. PullNotifier delivers smart, real-time PR updates directly to your Slack channels, cutting through the clutter so your team can focus on what matters. Cut your review delays by up to 90% and accelerate your development cycles by visiting https://pullnotifier.com.